[C++] [WMI] Windows Storage Management
2012/03/11 コメントを残す
CreateFIle API を使うとき、多くの場合では第一引数にファイル パスを渡してファイルを開きます。CreateFile の処理は内部的に Windows カーネルのオブジェクト マネージャーが第一引数の文字列をデバイス オブジェクトとして解釈し、I/O マネージャーが適当なドライバーにリダイレクトするという流れになっています。例えば、指定したファイルのあるボリュームが NTFS フォーマットだったら ntfs.sys が処理し、UNC パスだったら mrxsmb.sys が処理したりという感じです。厳密には誤りがあるかもしれませんが、大枠はこんな感じです。
CreateFile は、ファイル システムだけでなくデバイスへ直接アクセスすることもできます。ボリュームやディスクへのダイレクト I/O を行なえるわけです。シリアル ケーブルの通信なんかもそうですね。詳しくは MSDN で CreateFile を見て下さい。
CreateFile function
http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa363858(v=vs.85).aspx
ダイレクト I/O を使うと、フォーマットされていないボリュームや、パーティショニングされていないディスクに対して読み書きが可能になります。いわゆる RAW ディスクというやつで、ファイル システム ドライバーを必要としないわけです。この場合、上記 MSDN ページに書いてありますが CreateFile の第一引数に \\.\C: とか \\.\PhysicalDrive0 というような文字列を渡します。前者がボリューム デバイスを開く場合で、後者がディスク デバイスを開く場合です。
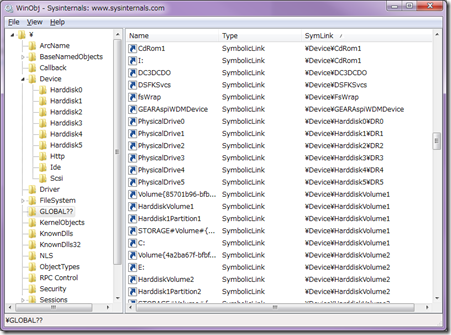
この文字列は、デバイス オブジェクトを直接示しているのではなく、デバイス オブジェクトへのシンボリック リンクの名前を示しています。デバイス オブジェクトについては、お馴染み Winobj で見ることができます。
Winobj
http://technet.microsoft.com/en-us/sysinternals/bb896657
上の画面だと、例えば以下のようなシンボリック リンクを確認できます。
\GLOBAL??\C: ⇒ \Device\HarddiskVolume1
\GLOBAL??\PhysicalDrive0 ⇒ \Device\Harddisk0\DR0
\GLOBAL?? というのは、オブジェクト マネージャーの解釈する名前空間です。が、Windows API はこの名前空間を解釈することができません。このため、\\.\ という接頭辞をつけるルールになっていて、CreateFile はこれを \GLOBAL?? という名前空間に変換してオブジェクト マネージャーに渡します。上の例で行けば、以下のような流れがあるわけです。
\\.\PhysicalDrive0 ⇒ \GLOBAL??\PhysicalDrive0 ⇒ \Device\Harddisk0\DR0
オブジェクト マネージャーが管理するオブジェクトについては、カーネル デバッガーの !object コマンドでも確認可能です。上記画面キャプチャと同じ環境でのカーネル デバッガーの出力を抜粋します。OS は Windows 7 SP1 64bit です。
まずは C: について。シンボリック リンクが HarddiskVolume0 を指していて、HarddiskVolume0 は volmgr.sys のデバイス オブジェクトであることが分かります。
0: kd> !driveinfo c:
Drive c:, DriveObject fffff8a00029c420
Directory Object: fffff8a000008060 Name: C:
Target String is ‘\Device\HarddiskVolume1’
Drive Letter Index is 3 (C:)
Volume DevObj: fffffa8007cc39a0
Vpb: fffffa8007cc0820 DeviceObject: fffffa8007fd0030
FileSystem: \FileSystem\Ntfs
*************************************************************************
*** ***
*** ***
*** Your debugger is not using the correct symbols ***
*** ***
*** In order for this command to work properly, your symbol path ***
*** must point to .pdb files that have full type information. ***
*** ***
*** Certain .pdb files (such as the public OS symbols) do not ***
*** contain the required information. Contact the group that ***
*** provided you with these symbols if you need this command to ***
*** work. ***
*** ***
*** Type referenced: ntfs!VOLUME_DEVICE_OBJECT ***
*** ***
*************************************************************************
Cannot get ntfs!VOLUME_DEVICE_OBJECT.Vcb @ fffffa8007fd00300: kd> !object \GLOBAL??\C:
Object: fffff8a00029c420 Type: (fffffa8006ca8de0) SymbolicLink
ObjectHeader: fffff8a00029c3f0 (new version)
HandleCount: 0 PointerCount: 1
Directory Object: fffff8a000008060 Name: C:
Target String is ‘\Device\HarddiskVolume1’
Drive Letter Index is 3 (C:)0: kd> !object \device\harddisk1\partition1
Object: fffff8a00029cd10 Type: (fffffa8006ca8de0) SymbolicLink
ObjectHeader: fffff8a00029cce0 (new version)
HandleCount: 0 PointerCount: 1
Directory Object: fffff8a0001f8060 Name: Partition1
Target String is ‘\Device\HarddiskVolume1’0: kd> !object \Device\HarddiskVolume1
Object: fffffa8007cc39a0 Type: (fffffa8006d32c90) Device
ObjectHeader: fffffa8007cc3970 (new version)
HandleCount: 0 PointerCount: 9
Directory Object: fffff8a000010920 Name: HarddiskVolume10: kd> !devobj fffffa8007cc39a0
Device object (fffffa8007cc39a0) is for:
HarddiskVolume1*** ERROR: Module load completed but symbols could not be loaded for spgu.sys
\Driver\volmgr DriverObject fffffa8007b617c0
Current Irp 00000000 RefCount 30480 Type 00000007 Flags 00201150
Vpb fffffa8007cc0820 Dacl fffff9a10033f0d0 DevExt fffffa8007cc3af0 DevObjExt fffffa8007cc3c58 Dope fffffa8007cc4820 DevNode fffffa8007ccda90
ExtensionFlags (0x00000800)
Unknown flags 0x00000800
AttachedDevice (Upper) fffffa8007ccea40 \Driver\fvevol
Device queue is not busy.
次に PhysicalDrive0 について。
PhysicalDrive0 が \Device\Harddisk0\DR0 という disk.sys のデバイス オブジェクトにリンクしていることが分かります。この DR0 というのがディスクのデバイス オブジェクトになるわけですが、NT4 の命名規約との互換性のためか、\Device\Harddisk0\Partition0 というシンボリック リンクも DR0 にリンクしています。このため、パーティション番号は 1 から始まることになります。DR が何の略なのかちょっと調べましたが出てきませんでした。知っている人教えて下さいー。
0: kd> !object \GLOBAL??\PhysicalDrive0
Object: fffff8a000154fe0 Type: (fffffa8006ca8de0) SymbolicLink
ObjectHeader: fffff8a000154fb0 (new version)
HandleCount: 0 PointerCount: 1
Directory Object: fffff8a000008060 Name: PhysicalDrive0
Target String is ‘\Device\Harddisk0\DR0’0: kd> !object \Device\Harddisk0\DR0
Object: fffffa8007e7c060 Type: (fffffa8006d32c90) Device
ObjectHeader: fffffa8007e7c030 (new version)
HandleCount: 0 PointerCount: 4
Directory Object: fffff8a0001f8eb0 Name: DR00: kd> !devobj fffffa8007e7c060
Device object (fffffa8007e7c060) is for:
DR0 \Driver\Disk DriverObject fffffa8007cbce70
Current Irp 00000000 RefCount 0 Type 00000007 Flags 01002050
Vpb fffffa8007cbdb80 Dacl fffff9a100303ae0 DevExt fffffa8007e7c1b0 DevObjExt fffffa8007e7c858 Dope fffffa8007cbdb10
ExtensionFlags (0x00000800)
Unknown flags 0x00000800
AttachedDevice (Upper) fffffa8007e7cb90 \Driver\partmgr
AttachedTo (Lower) fffffa8007abd420 \Driver\ACPI
Device queue is not busy.0: kd> !object \Device\Harddisk0\Partition0
Object: fffff8a000154200 Type: (fffffa8006ca8de0) SymbolicLink
ObjectHeader: fffff8a0001541d0 (new version)
HandleCount: 0 PointerCount: 1
Directory Object: fffff8a0001f8eb0 Name: Partition0
Target String is ‘\Device\Harddisk0\DR0’
なお、この辺の動作は「インサイド Windows 第四版 第 10 章 ストレージ管理」 に書いてあります。
ダイレクト I/O 周りの動作をデバッグしてもいいのですが、それは今後検討するとして、今回はシンボリック リンク名とドライブ文字のマッピングについてのプログラムを書きました。例えば、C: ドライブは PhysicalDrive 何番なのか、逆に PhysicalDrive1 にはどのドライブ文字が割り当てられているのか、という点について調べようとすると、ビルトインでいいツールがないのです。いちいち Winobj やらデバッガーを使うのも鶏を割くのに牛刀を用いる感じがします。
プログラムはこんな感じです。
ご覧のとおり WMI を使いました。WMI だと間接的に情報を取ってくることになり、一次情報を取っていない気がして本当は嫌なのですが、他にシンプルな方法が思い浮かばなくて仕方なく、です。VDS である程度の情報は取ってこれるんですけどね。
なお、このプログラムでは CD-ROM ドライブや、ドライブ文字が割り当てられていないボリュームが出力されません。ダメダメです。
//
// wmidata.cpp
//#include <Windows.h>
#include <stdio.h>
#include <strsafe.h>#include <comdef.h>
#include <Wbemidl.h>#pragma comment(lib, "wbemuuid.lib")
typedef struct _DRIVEINFO {
WCHAR DriveLetter;
UINT DiskIndex;
UINT PartitionIndex;
} DRIVEINFO, *PDRIVEINFO;class CWmiService {
private:
IWbemLocator *mLocator;
IWbemServices *mService;public:
CWmiService();
~CWmiService();BOOL Initialize();
inline operator IWbemServices*() const {
return mService;
}IWbemClassObject *GetObject(IWbemClassObject*, LPCWSTR);
UINT GetUint32(IWbemClassObject*, LPCWSTR);
VOID GetString(IWbemClassObject*, LPCWSTR, PWSTR, ULONG);ULONG GetCount(LPCWSTR);
};
CWmiService::CWmiService()
: mLocator(NULL), mService(NULL)
{}CWmiService::~CWmiService() {
if ( mLocator ) mLocator->Release();
if ( mService ) mService->Release();
CoUninitialize();
}// http://technet.microsoft.com/ja-jp/library/aa390423(v=vs.85).aspx
BOOL CWmiService::Initialize() {
HRESULT Result;
Result= CoInitializeEx(0, COINIT_MULTITHREADED);
if ( FAILED(Result) ) {
wprintf(L"CoInitializeEx failed – 0x%08x\n", Result);
return FALSE;
}Result= CoInitializeSecurity(NULL, -1, NULL, NULL,
RPC_C_AUTHN_LEVEL_DEFAULT,
RPC_C_IMP_LEVEL_IMPERSONATE,
NULL, EOAC_NONE, NULL);
if ( FAILED(Result) ) {
wprintf(L"CoInitializeSecurity failed – 0x%08x\n", Result);
return FALSE;
}
Result = CoCreateInstance(CLSID_WbemLocator,
0, CLSCTX_INPROC_SERVER,
IID_IWbemLocator, (LPVOID *)&mLocator);
if ( FAILED(Result) ) {
wprintf(L"CoCreateInstance failed – 0x%08x\n", Result);
return FALSE;
}Result= mLocator->ConnectServer(_bstr_t(L"ROOT\\CIMV2"),
NULL, NULL, 0, NULL, 0, 0,&mService);
if ( FAILED(Result) ) {
wprintf(L"IWbemLocator::ConnectServer failed – 0x%08x\n", Result);
return FALSE;
}Result= CoSetProxyBlanket(mService,
RPC_C_AUTHN_WINNT,
RPC_C_AUTHZ_NONE,
NULL,
RPC_C_AUTHN_LEVEL_CALL,
RPC_C_IMP_LEVEL_IMPERSONATE,
NULL, EOAC_NONE);
if ( FAILED(Result) ) {
wprintf(L"CoSetProxyBlanket failed – 0x%08x\n", Result);
return FALSE;
}return TRUE;
}IWbemClassObject *CWmiService::GetObject(IWbemClassObject *Object, LPCWSTR Property) {
HRESULT Result;
IWbemClassObject *Ret= NULL;
VARIANT Value;Result= Object->Get(Property, 0, &Value, NULL, NULL);
if ( FAILED(Result) ) {
wprintf(L"IWbemClassObject::Get failed – 0x%08x\n", Result);
return NULL;
}Result= mService->GetObject(Value.bstrVal,
WBEM_FLAG_RETURN_WBEM_COMPLETE,
NULL, &Ret, NULL);
if ( FAILED(Result) ) {
wprintf(L"IWbemServices::GetObject failed – 0x%08x\n", Result);
Ret= NULL;
}VariantClear(&Value);
return Ret;
}UINT CWmiService::GetUint32(IWbemClassObject *Object, LPCWSTR Property) {
LRESULT Result;
UINT Ret= 0;
VARIANT Value;Result= Object->Get(Property, 0, &Value, NULL, NULL);
if ( SUCCEEDED(Result) )
Ret= Value.uintVal;
else
wprintf(L"IWbemClassObject::Get failed – 0x%08x\n", Result);VariantClear(&Value);
return Ret;
}VOID CWmiService::GetString(IWbemClassObject *Object, LPCWSTR Property,
PWSTR Buffer, ULONG BufferLength) {
LRESULT Result;
VARIANT Value;Result= Object->Get(Property, 0, &Value, NULL, NULL);
if ( SUCCEEDED(Result) ) {
StringCchCopy(Buffer, BufferLength, Value.bstrVal);
VariantClear(&Value);
}
else {
wprintf(L"IWbemClassObject::Get failed – 0x%08x\n", Result);
return;
}
}ULONG CWmiService::GetCount(LPCWSTR Query) {
LRESULT Result;
ULONG Ret= 0;
CONST INT BatchCount= 100;
IWbemClassObject *Object[BatchCount];
IEnumWbemClassObject *Enumerator= NULL;
Result= mService->ExecQuery(bstr_t("WQL"), bstr_t(Query),
WBEM_FLAG_FORWARD_ONLY | WBEM_FLAG_RETURN_IMMEDIATELY,
NULL, &Enumerator);
if ( FAILED(Result) ) {
wprintf(L"IWbemServices::ExecQuery failed – 0x%08x\n", Result);
return 0;
}// http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa394175(v=vs.85).aspx
while ( Enumerator ) {
ULONG Count= 0;
Result= Enumerator->Next(WBEM_INFINITE, BatchCount, Object, &Count);
if ( Count==0 ) break;
if ( FAILED(Result) ) {
wprintf(L"IEnumWbemClassObject::Next failed – 0x%08x\n", Result);
break;
}
Ret+= Count;for ( ULONG i=0 ; i<Count ; ++i )
Object[i]->Release();
}Enumerator->Release();
return Ret;
}typedef int (__cdecl *PCOMPAREFUNC)(const void *, const void *);
int CompareDriveInfo_Index(CONST PDRIVEINFO p1, CONST PDRIVEINFO p2) {
if ( p1->DiskIndex==p2->DiskIndex )
return p1->PartitionIndex-p2->PartitionIndex;
else
return p1->DiskIndex-p2->DiskIndex;
}int CompareDriveInfo_Drive(CONST PDRIVEINFO p1, CONST PDRIVEINFO p2) {
return p1->DriveLetter-p2->DriveLetter;
}// http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa394175(v=vs.85).aspx
VOID DumpDiskDriveMapping() {
CONST WCHAR QUERY_MAPPING[]= L"SELECT * FROM Win32_LogicalDiskToPartition";
LRESULT Result;
ULONG Count= 0;
IEnumWbemClassObject *Enumerator= NULL;
IWbemClassObject **Object= NULL;
IWbemClassObject *Partition= NULL; // Antecedent
IWbemClassObject *LogicalDisk= NULL; // Dependent
PDRIVEINFO DriveInfo= NULL;
ULONG i;CWmiService wmi;
wmi.Initialize();
ULONG MappedDrives= wmi.GetCount(QUERY_MAPPING);
if ( MappedDrives==0 ) {
wprintf(L"No drives?\n");
goto cleanup;
}DriveInfo= new DRIVEINFO[MappedDrives];
Object= new IWbemClassObject*[MappedDrives];
if ( !DriveInfo || !Object ) {
wprintf(L"Memory allocation error – 0x%08x\n", GetLastError());
goto cleanup;
}Result= ((IWbemServices*)wmi)->ExecQuery(
bstr_t("WQL"), bstr_t(QUERY_MAPPING),
WBEM_FLAG_FORWARD_ONLY | WBEM_FLAG_RETURN_IMMEDIATELY,
NULL, &Enumerator);
if ( FAILED(Result) ) {
wprintf(L"IWbemServices::ExecQuery failed – 0x%08x\n", Result);
goto cleanup;
}Result= Enumerator->Next(WBEM_INFINITE, MappedDrives, Object, &Count);
if ( FAILED(Result) ) {
wprintf(L"IEnumWbemClassObject::Next failed – 0x%08x\n", Result);
goto cleanup;
}
for ( i=0 ; i<Count ; ++i ) {
Partition= wmi.GetObject(Object[i], L"Antecedent");
if ( Partition ) {
// http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa394135(v=vs.85).aspx
DriveInfo[i].PartitionIndex= wmi.GetUint32(Partition, L"Index");
DriveInfo[i].DiskIndex= wmi.GetUint32(Partition, L"DiskIndex");
Partition->Release();
}LogicalDisk= wmi.GetObject(Object[i], L"Dependent");
if ( LogicalDisk ) {
// http://msdn.microsoft.com/en-us/library/windows/desktop/aa394173(v=vs.85).aspx
WCHAR Drive[3];
wmi.GetString(LogicalDisk, L"DeviceID", Drive, 2);
DriveInfo[i].DriveLetter= Drive[0];
LogicalDisk->Release();
}Object[i]->Release();
}qsort(DriveInfo, Count, sizeof(DRIVEINFO), (PCOMPAREFUNC)CompareDriveInfo_Index);
// http://otndnld.oracle.co.jp/document/products/oracle10g/102/windows/B25695-02/ap_raw.htm
int diskindex= -1;
for ( i=0 ; i<Count ; ++i ) {
if ( diskindex!=DriveInfo[i].DiskIndex ) {
wprintf(L"\n\\\\.\\PhysicalDrive%d\n", DriveInfo[i].DiskIndex);
diskindex= DriveInfo[i].DiskIndex;
}wprintf(L" \\\\.\\%c: => \\Device\\Harddisk%d\\Partition%d\n",
DriveInfo[i].DriveLetter,
DriveInfo[i].DiskIndex,
DriveInfo[i].PartitionIndex+1,
DriveInfo[i].DiskIndex);
}//putwchar(L’\n’);
//qsort(DriveInfo, Count, sizeof(DRIVEINFO), (PCOMPAREFUNC)CompareDriveInfo_Drive);
//
//for ( i=0 ; i<Count ; ++i ) {
// wprintf(L" %c: => \\Device\\Harddisk%d\\Partition%d : \\PhysicalDrive%d\n",
// DriveInfo[i].DriveLetter,
// DriveInfo[i].DiskIndex,
// DriveInfo[i].PartitionIndex+1,
// DriveInfo[i].DiskIndex);
//}cleanup:
if ( Object ) delete [] Object;
if ( DriveInfo ) delete [] DriveInfo;
if ( Enumerator ) Enumerator->Release();}
出力結果はこんな感じになります。
出力例 1.
\\.\PhysicalDrive0
\\.\V: => \Device\Harddisk0\Partition2\\.\PhysicalDrive1
\\.\C: => \Device\Harddisk1\Partition1
\\.\H: => \Device\Harddisk1\Partition2
\\.\T: => \Device\Harddisk1\Partition3\\.\PhysicalDrive2
\\.\E: => \Device\Harddisk2\Partition1
\\.\W: => \Device\Harddisk2\Partition2\\.\PhysicalDrive3
\\.\F: => \Device\Harddisk3\Partition1
出力例 2.
\\.\PhysicalDrive0
\\.\C: => \Device\Harddisk0\Partition2
\\.\N: => \Device\Harddisk0\Partition4
\\.\O: => \Device\Harddisk0\Partition4\\.\PhysicalDrive1
\\.\E: => \Device\Harddisk1\Partition1
\\.\F: => \Device\Harddisk1\Partition2
\\.\G: => \Device\Harddisk1\Partition3
\\.\H: => \Device\Harddisk1\Partition4
\\.\I: => \Device\Harddisk1\Partition5
\\.\J: => \Device\Harddisk1\Partition6
\\.\K: => \Device\Harddisk1\Partition7
\\.\L: => \Device\Harddisk1\Partition8
\\.\M: => \Device\Harddisk1\Partition9
パーティション番号が抜けているところは、ドライブ文字が割り当てられていないボリュームです。
出力例 2. で \Device\Harddisk0\Partition4 が 2 つあるのは、これが拡張パーティションで、論理ドライブが 2 つあるという意味です。MBR の制限ですね。一方 PhysicalDrive1 は GPT パーティショニングなので、9 つのパーティションでも問題なしです。
今回は C++ プログラムで処理しましたが、WMI については、やはり PowerShell でアクセスするのが一番楽です。他にも wmic やら wbemtest、VB スクリプトを使うなどの方法もあります。しかし、Windows 7 (2008 R2) なら PowerShell の Get-WMIObject と Set-WmiInstance コマンドレットを使わない手はありません。例え起動が遅いと言われようとも、これだけのために PowerShell を使う価値はあります。
ソース中のコメントに入れてありますが、今回のプログラムは Win32_DiskDriveToDiskPartition クラスのインスタンスを適当に成形しているだけです。
PS > Get-WmiObject Win32_DiskDriveToDiskPartition | fl Antecedent,Dependent
Antecedent : \\ALANINE\root\cimv2:Win32_DiskDrive.DeviceID="\\\\.\\PHYSICALDRIVE1"
Dependent : \\ALANINE\root\cimv2:Win32_DiskPartition.DeviceID="Disk #1, Partition #0"Antecedent : \\ALANINE\root\cimv2:Win32_DiskDrive.DeviceID="\\\\.\\PHYSICALDRIVE1"
Dependent : \\ALANINE\root\cimv2:Win32_DiskPartition.DeviceID="Disk #1, Partition #1"Antecedent : \\ALANINE\root\cimv2:Win32_DiskDrive.DeviceID="\\\\.\\PHYSICALDRIVE1"
Dependent : \\ALANINE\root\cimv2:Win32_DiskPartition.DeviceID="Disk #1, Partition #2"Antecedent : \\ALANINE\root\cimv2:Win32_DiskDrive.DeviceID="\\\\.\\PHYSICALDRIVE0"
Dependent : \\ALANINE\root\cimv2:Win32_DiskPartition.DeviceID="Disk #0, Partition #0"
(2015/1/8 追記)
意外とこの記事へのアクセス数が多いこともあり、3 年近く前の記事への追記です。とても便利なビルトインのツールがありました。Windows Server 2003 のサポート ツールに含まれている dmdiag.exe です。
Windows Server 2003 Service Pack 2 32-bit Support Tools
http://www.microsoft.com/en-us/download/details.aspx?id=15326
管理者権限で dmdiag.exe に -v オプションをつけて実行すると、ストレージ周りの情報をかなり詳細にダンプしてくれます。古いツールですが、少なくとも Windows 8.1 (Server 2012 R2) までなら動作します。以下、出力の抜粋です。
d:\MSWORK>.\dmdiag -v
---------- Computer Name and OS Version ----------
Computer name: GUANOSINE
NT build: 9200
CPU Type: x86
DMDIAG Version: 5.2.3790.0 shp
---------- LDM File Versions ----------
(..snip..)
---------- Mount Points ----------
---------- Drive Letter Usage, Drive Type ----------
C: = \Device\HarddiskVolume6 [Fixed]
D: = \Device\HarddiskVolume8 [Fixed]
E: = \Device\HarddiskVolume4 [Fixed]
Q: = \Device\CdRom0 [CDRom]
U: = \Device\HarddiskVolume3 [Fixed]
V: = \Device\HarddiskVolume2 [Fixed]
W: = \Device\HarddiskVolume7 [Fixed]
X: = \Device\HarddiskVolume5 [Fixed]
---------- Consolidated LDM Configuration Data ----------
(..snip..)
---------- \Device\Harddisk0 ----------
\Device\Harddisk0\DR0 (Device)
\Device\Harddisk0\Partition0 (SymbolicLink) -> \Device\Harddisk0\DR0
\Device\Harddisk0\Partition1 (SymbolicLink) -> \Device\HarddiskVolume1
\Device\Harddisk0\Partition2 (SymbolicLink) -> \Device\HarddiskVolume2
---------- \Device\Harddisk1 ----------
\Device\Harddisk1\DR1 (Device)
\Device\Harddisk1\Partition0 (SymbolicLink) -> \Device\Harddisk1\DR1
\Device\Harddisk1\Partition1 (SymbolicLink) -> \Device\HarddiskVolume3
---------- \Device\Harddisk2 ----------
\Device\Harddisk2\DR2 (Device)
\Device\Harddisk2\Partition0 (SymbolicLink) -> \Device\Harddisk2\DR2
\Device\Harddisk2\Partition1 (SymbolicLink) -> \Device\HarddiskVolume4
\Device\Harddisk2\Partition2 (SymbolicLink) -> \Device\HarddiskVolume5
---------- \Device\Harddisk3 ----------
\Device\Harddisk3\DR3 (Device)
\Device\Harddisk3\Partition0 (SymbolicLink) -> \Device\Harddisk3\DR3
\Device\Harddisk3\Partition1 (SymbolicLink) -> \Device\HarddiskVolume6
\Device\Harddisk3\Partition2 (SymbolicLink) -> \Device\HarddiskVolume7
\Device\Harddisk3\Partition3 (SymbolicLink) -> \Device\HarddiskVolume8
---------- Partition Table Info Disk 0 ----------
14,593 Cylinders
255 Tracks/Cylinder
63 Sectors/Track
512 Bytes/Sector
12 MediaType
234,436,545 Sectors (total)
120,031,511,040 Bytes (total)
117,218,273 KB
114,471 MB
111.8 GB0 StartingOffset
120,034,123,776 PartitionLength
0 HiddenSectors
0 PartitionNumber
0 PartitionType
0 BootIndicator
0 RecognizedPartition
0 RewritePartitionMBR PartitionStyle
4 PartitionCount
3afc7bc6 SignatureStarting Partition Hidden Total Partition Partition Boot Recognized Rewrite
Offset (bytes) Length (bytes) Sectors Sectors Number Type (HEX) Indicator Partition Partition1,048,576 104,857,600 2,048 204,800 0 0x07 1 1 0
105,906,176 119,925,637,120 206,848 234,229,760 1 0x07 0 1 0
0 0 0 0 2 0x00 0 0 0
0 0 0 0 3 0x00 0 0 0120,031,511,040 Bytes (234436545 sectors) Geometric size
120,034,123,776 Bytes (234441648 sectors) True size (measured)
120,034,123,776 Bytes (234441648 sectors) Reported size (Partition0)
0 Bytes ( 0 sectors) missing/wasted---------- Partition Table Info Disk 1 ----------
(..snip..)
---------- Partition Table Info Disk 2 ----------
(..snip..)
---------- Partition Table Info Disk 3 ----------
(..snip..)
---------- DMIO Kernel List ----------
(..snip..)