A Quick Guide to USB Port Symbols, Logos, and Icons

Here is our comprehensive breakdown of the symbols and logos commonly found on USB-compatible laptops and devices like connection ports, storage drives, charging cables, and more. Our hope is that knowledge of these icons can help you make an informed decision on which device connection type is right for your system, and what the symbols really mean.
A short background on who sets the standard.
The USB-IF (USB Implementers Forum, Inc.) is an organization founded by the companies that developed the Universal Serial Bus specification. Formed to provide a support structure and forum for developing USB technology, the USB-IF outlines compliance for USB-compatible devices. Responsible for designating the common and accepted practice in labeling ports, cables, and devices, the USB-IF sets the requirements for clear and understandable logo usage to promote quality of product.
What exactly am I looking for?
If you take a close-up look at your USB devices and ports, you may notice the USB symbol marked to indicate the compatibility and capabilities of the port. It started quite simply as a three-pronged pathway or “Trident Logo” as it is referred to by the USB-IF. This trident leads from a circle to three recognizable shapes: another (smaller) circle, an arrow-like triangle, and a square.
From a design perspective, this symbol indicates that a basic USB connection port has the ability to connect to various cables and devices.
What are the main icons I need to know?
It’s important to understand that based on the stage of their release, or the transfer speeds they were built for, different USB generations of cables will provide different features, separated generally by data transfer, audio, video, and power delivery.
Five of the main icons to keep an eye out for in approved USB iconography are:
HighSpeed USB
Seen indicated also indicated as Hi-Speed, this USB connection is used for the USB 2.0 standard, these icons are regularly seen on devices with 480 Mbps bandwidth.

SuperSpeed USB
The upgrade from Hi-Speed USB, these connections represent the USB 3.0 standard also known as (USB 3.1 Gen 1, USB 3.2 Gen 1), stylized with a capitalized and italicized SS, and including the data transfer speed capability of 5 Gbps atop the classic middle triangle prong.

SuperSpeed+ USB
Twice the speed of USB 3.0 standard also known as (USB 3.1 Gen 2, USB 3.2 Gen 2), stylized with a capitalized and italicized SS, and including the data transfer speed capability of 10 Gbps atop the classic middle triangle prong.

SuperSpeed with Power Delivery
Not to be confused with its classic SuperSpeed counterpart, this designation carries the same stylized icon encased within a battery-like shell logo including a trademark symbol.

SuperSpeed+ with Power Delivery
Similar to its SuperSpeed+ counterpart, this designation carries the same stylized icon encased within a battery-like shell logo including a trademark symbol.

USB4
The most modern of USB connection types, these devices will be marked clearly with their transfer speed capability and the classic USB trident.




Fast-charging
Anytime a classic black lightning bolt is seen next to a USB-A or USB-C connector, you know the port offers fast-charging for mobile devices whether it’s a phone, tablet, or other connected peripheral.
DisplayPort Alt Mode
Rare to see but equally important is a black D icon with a white P inscribed within. This indicates a port supports DP Alt Mode for video delivery.

Form Factor & Common Connections
USB-C caters to devices with a smaller more compact form factor such as many modern laptops like Google’s Chromebooks and Apple’s new M1 Macs. Though USB-C is becoming more and more commonplace in connection with new technologies, not all devices require a USB-C cable. That said, smart phones, tablets, flash drives, SD card readers, power banks, external hard drives, and even some headphones are regularly using USB-C connections for their function.
Alternate Modes
With alternate modes, USB Type-C connector pins can carry other signals such as DisplayPort Alt Mode (often labeled DP Alt Mode) which provides the ability for DP laptops or tablets to connect directly to an external monitor via USB-C ports.
With each new generation of USB-C, we’ve seen different specifications that center around transfer speeds and compatibility. Here is a breakdown of USB-C transfer speeds:
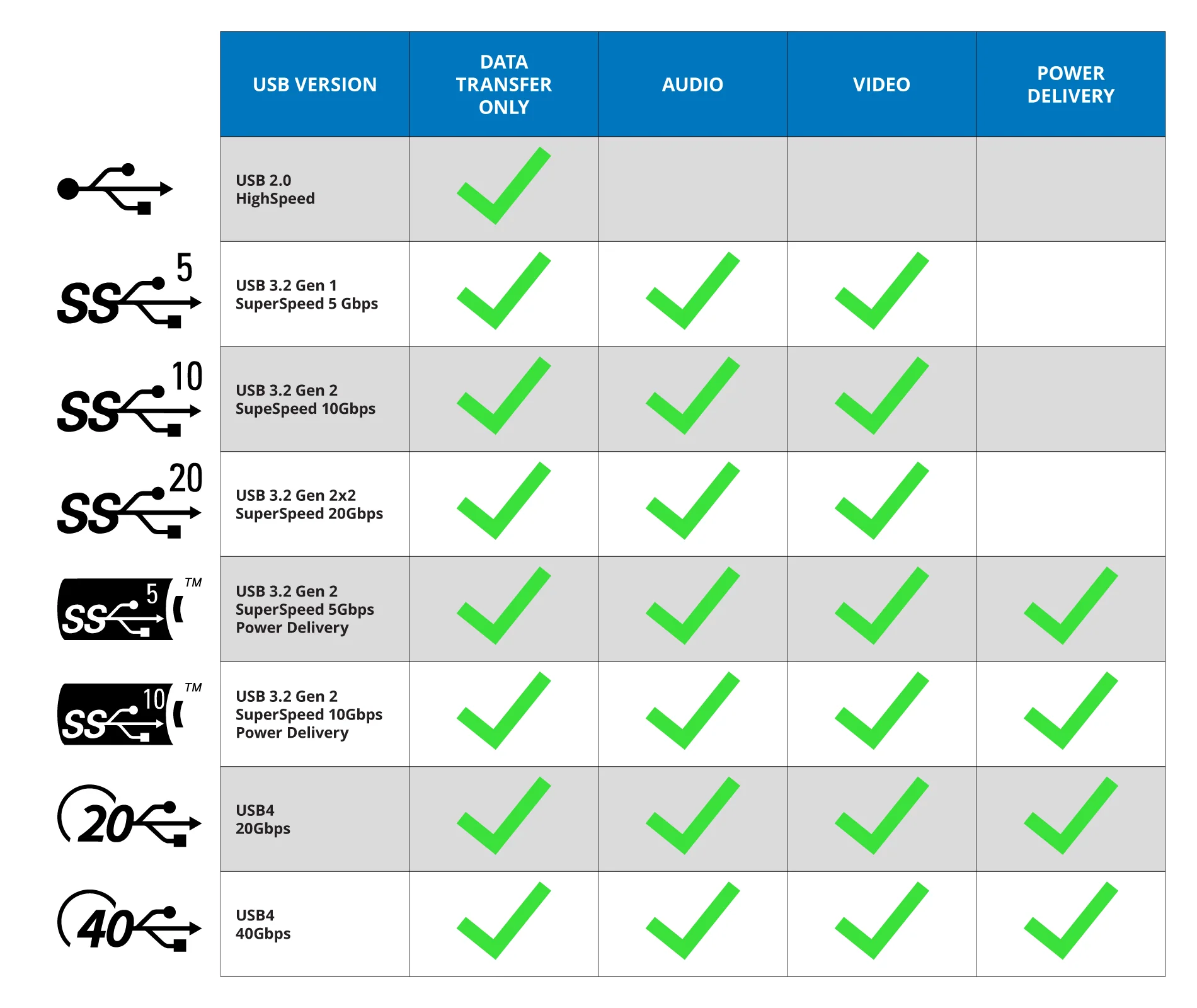
Compatibility Reference Chart
USB-C supports USB4, 3.2, and 3.1 but is also backward compatible with both USB 3.0 and USB 2.0. Below is a chart indicating which USB versions carry which features.
You’re ready!
Bookmark this page for a quick reference in the future when checking out new cables for your home set-up or a new laptop for remote work.
For the full USB-IF Usage Guidelines, you can find documentation here:
If the reading above looks too dense, drop a question on our social media platform and we’ll be happy to clear up any confusion! Otherwise, you can check out our collection of USB-compatible devices here.
| USB Version | Also Known As | Connector Types | Max Transfer Speed | Max Cable Length |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| USB 1.1 | Full Speed USB | USB-A | 12 Mbps | 3 m |
| USB 2.0 | Hi-Speed USB | USB-A USB-C | 480 Mbps | 5 m |
| USB 3.2 Gen 1 | USB 3.0 USB 3.1 Gen 1 SuperSpeed | USB-A USB-C | 5 Gbps | 3 m |
| USB 3.2 Gen 2 | USB 3.1 USB 3.1 Gen 2 SuperSpeed+ Super Speed 10Gbps | USB-A USB-C | 10 Gbps | 3 m |
| USB 3.2 2x2 | USB 3.2 SuperSpeed 20Gbps | USB-C | 20 Gbps | 3 m |
| USB4 | USB4 Gen 2x2 USB4 20Gbps | USB-C | 20Gbps | .8 m |
| USB4 | USB4 Gen 3x2 USB4 40Gbps | USB-C | 40Gbps | .8 m |

